Earwax. It’s not exactly the most glamorous topic, but this sticky substance holds secrets about your health that may surprise you. From detecting genetic traits to offering early warnings for serious diseases, earwax may one day become a diagnostic goldmine for healthcare professionals.
This article explores what earwax is, its fascinating connection to your health, and why researchers are calling it the “lipid-rich fingerprint” of our bodies. Stick around to discover what this often-overlooked bodily secretion can reveal about your well-being.
What Exactly Is Earwax?
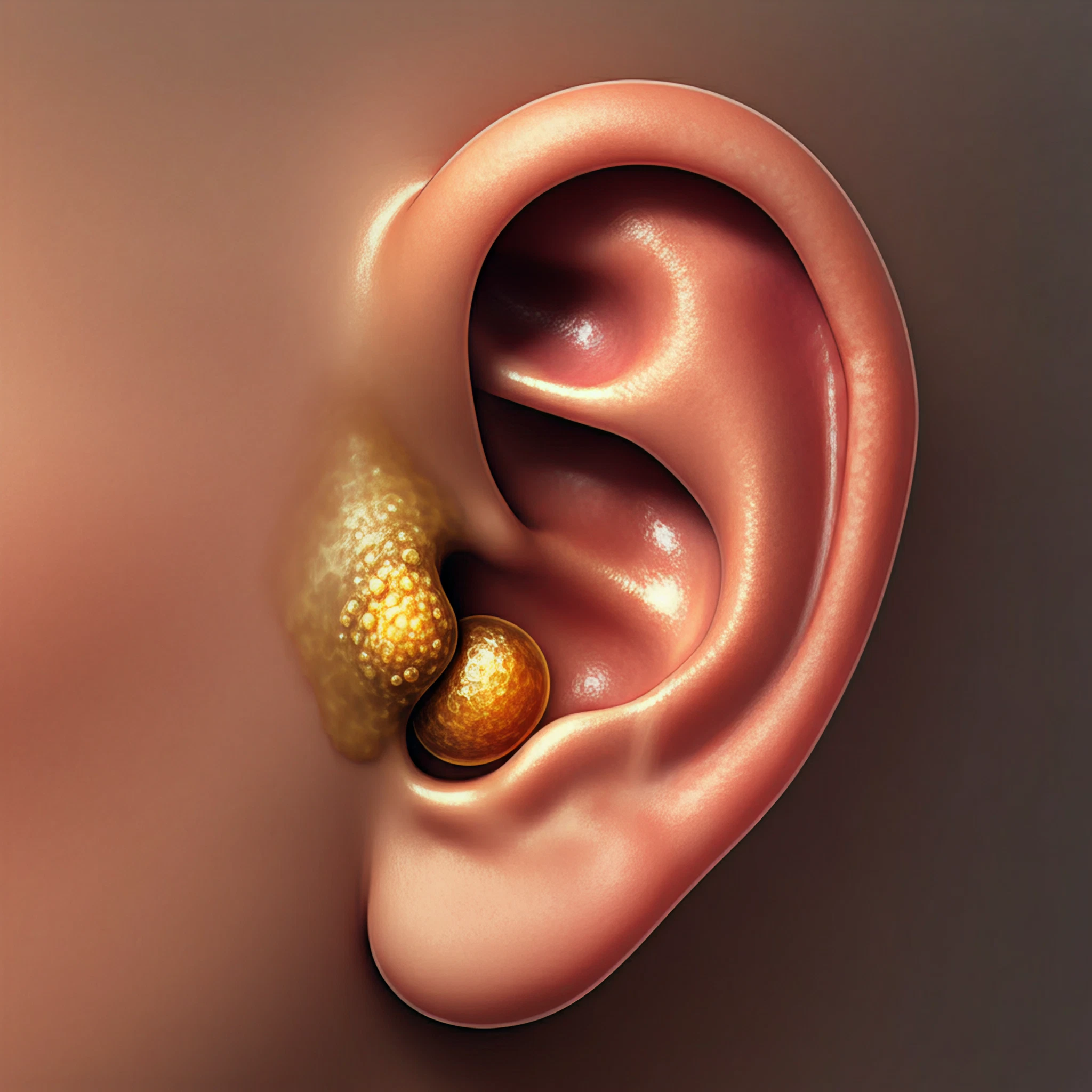
The scientific name for earwax is cerumen, a unique mix of secretions from the ceruminous and sebaceous glands in the ear canal. It’s made up of sweat, oil, dead skin cells, and tiny bits of hair, resulting in a gooey substance that most of us regard with mild discomfort.
But earwax is far more than an unpleasant inconvenience. It plays an essential role in keeping the ear canal:
- Clean and lubricated by trapping dirt and debris.
- Protected from infections by preventing bacteria and fungi from entering the ear.
- Guarded against insects or other foreign objects.
Interestingly, the characteristics of your earwax, such as its texture and smell, can also reflect key details about your health and genetics.
The Types of Earwax
Did you know your earwax type is determined by your genetic makeup? Broadly, there are two categories:
- Wet Earwax: Yellow or orange, sticky, and more common in people of European or African descent.
- Dry Earwax: Grayish and crumbly, typically found in people of East Asian or Native American origin.
The ABCC11 gene, which is responsible for earwax type, is also linked to whether or not a person’s armpits produce odor. Fascinatingly, about 2% of people—mainly in the “dry” earwax group—don’t produce body odor.
What Earwax Can Tell Us About Our Health
Recent research has revealed just how valuable earwax can be in diagnosing and understanding various medical conditions. Here’s a closer look at what’s been uncovered so far:
1. Risk for Breast Cancer
A 2010 study from the Tokyo Institute of Technology suggested that Japanese women with “wet” earwax were more likely to carry a gene linked to breast cancer. However, further research is needed to establish a solid connection.
2. Maple Syrup Urine Disease
This rare genetic disorder prevents the body from breaking down specific amino acids. It gives urine a sweet smell resembling maple syrup. Remarkably, this condition can also be detected in earwax, which could make diagnosis cheaper and easier.
3. Diabetes and Heart Disease
Researchers have noted that earwax may act as an indicator for metabolic conditions like diabetes and heart diseases. Specific chemical compounds in earwax could eventually help doctors spot these illnesses early.
4. Ménière’s Disease
This debilitating inner ear condition can cause vertigo, nausea, and hearing loss. Scientists have recently discovered that earwax from patients with Ménière’s disease has altered levels of fatty acids. This breakthrough may lead to quicker and less invasive diagnostic methods.
5. Early Cancer Detection
Brazilian researchers are developing a test called a “cerumenogram,” which has been able to identify certain cancers like lymphoma and leukemia with surprising accuracy. By analyzing the volatile organic compounds in earwax, this promising tool could detect even precancerous changes.
Why Is Earwax Such a Good Diagnostic Tool?
Unlike blood and urine, earwax accumulates slowly in the ear canal, providing a long-term snapshot of the body’s metabolic changes. The lipid-rich composition of earwax also makes it an excellent repository for chemical substances that other bodily fluids may not capture as effectively.
According to Dr. Nelson Roberto Antoniosi Filho, a chemist researching earwax, this substance might one day diagnose multiple conditions—including cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, and diabetes—with a simple swab.
The Future of Earwax in Medicine
Though its full potential is still being explored, earwax could soon take a starring role in healthcare:
- Routine Testing: Diagnostic kits similar to COVID-19 tests may allow individuals to analyze their earwax at home to detect a range of conditions.
- Prevention through Early Diagnosis: Identifying precancerous stages or early signs of chronic diseases could significantly improve treatment outcomes.
- Personalized Medicine: Analyzing earwax over time could help doctors tailor treatments to individuals’ unique metabolic profiles.
A Word of Caution
While earwax is a treasure trove of health insights, self-diagnosing based solely on its color, texture, or smell isn’t advisable. If you notice unusual changes in your earwax, it’s best to consult a healthcare professional.
Understanding Your Body, One Detail at a Time
Who would have thought that earwax could hold such a wealth of information? It’s a vivid reminder that our bodies are designed to provide their own clues about what’s happening beneath the surface.
By paying attention to these subtle indicators, like the chemical makeup of earwax, science is unlocking new possibilities for understanding and diagnosing health conditions.
For more health tips rooted in science and accessible wellness info, be sure to check out additional resources on our site. Your body is talking to you. Are you ready to listen?